 Boost
C++ Libraries
Boost
C++ Libraries
...one of the most highly
regarded and expertly designed C++ library projects in the
world.
— Herb Sutter and Andrei
Alexandrescu, C++
Coding Standards
 Boost
C++ Libraries
Boost
C++ Libraries
...one of the most highly
regarded and expertly designed C++ library projects in the
world.
— Herb Sutter and Andrei
Alexandrescu, C++
Coding Standards
(Testing program at perf.cpp.)
We ran tests to measure the performance of the containers of Boost.PolyCollection in two scenarios:
std::for_each
and boost::poly_collection::for_each (with and without type
restitution).
As a comparison baseline we used containers and facilities from the standard library and Boost (details below). Tests were run on a Windows 10 machine with 8GB RAM and an Intel Core i5-8265U CPU @1.60GHz (base frequency) for the following environments:
-O3 -DNDEBUG
ptr_vector
= boost::ptr_vector<base>
base_collection
= boost::base_collection<base>
T1 =
derived1, T2 = derived2,
T3 = derived3
struct base { virtual ~base()=default; virtual int operator()(int)const=0; }; struct derived1 final:base { derived1(int n):n{n}{} virtual int operator()(int)const{return n;} int n; }; struct derived2 final:base { derived2(int n):n{n}{} virtual int operator()(int x)const{return x*n;} int unused,n; }; struct derived3 final:base { derived3(int n):n{n}{} virtual int operator()(int x)const{return x*x*n;} int unused,n; };
func_vector
= std::vector<std::function<int(int)>>
function_collection
= boost::function_collection<int(int)>
T1 =
concrete1, T2 = concrete2,
T3 = concrete3
struct concrete1 { concrete1(int n):n{n}{} int operator()(int)const{return n;} int n; }; struct concrete2 { concrete2(int n):n{n}{} int operator()(int x)const{return x*n;} int unused,n; }; struct concrete3 { concrete3(int n):n{n}{} int operator()(int x)const{return x*x*n;} int unused,n; };
any_vector
= std::vector<boost::type_erasure::any<concept_>>
any_collection
= boost::any_collection<concept_>
T1 =
int, T2
= double, T3 = char
using concept_=boost::mpl::vector< boost::type_erasure::copy_constructible<>, boost::type_erasure::relaxed, boost::type_erasure::typeid_<>, boost::type_erasure::incrementable<> >;
variant_vector
= std::vector<std::variant<int,double,char>>
variant_collection
= boost::variant_collection<boost::mp11::mp_list<int,double,char>>
T1 =
int, T2
= double, T3 = char
Tests measure the time taken to insert n elements (n
between 102 and 107) from a source of values with types randomly selected from
T1, T2
and T3 with equal probability.
No reserve operation is done
before insertion. The figures show resulting times in nanoseconds/element.
The horizontal axis is logarithmic.
 Insertion, Visual Studio
2022 x64
Insertion, Visual Studio
2022 x64
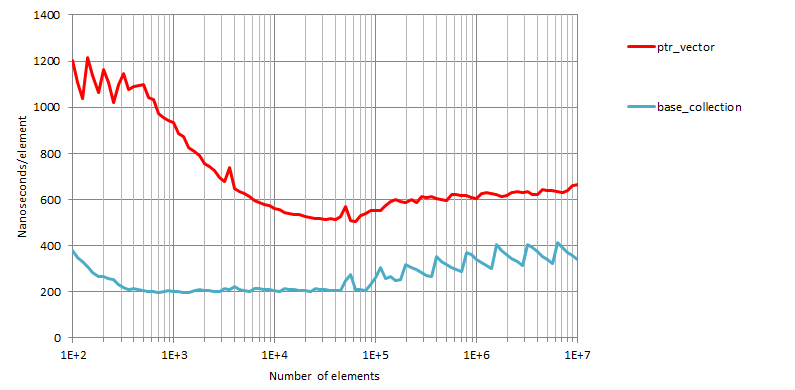 Insertion, GCC 13.2
x64
Insertion, GCC 13.2
x64
 Insertion, Clang 13.0
x64
Insertion, Clang 13.0
x64
 Insertion, Visual Studio
2022 x64
Insertion, Visual Studio
2022 x64
 Insertion, GCC 13.2
x64
Insertion, GCC 13.2
x64
 Insertion, Clang 13.0
x64
Insertion, Clang 13.0
x64
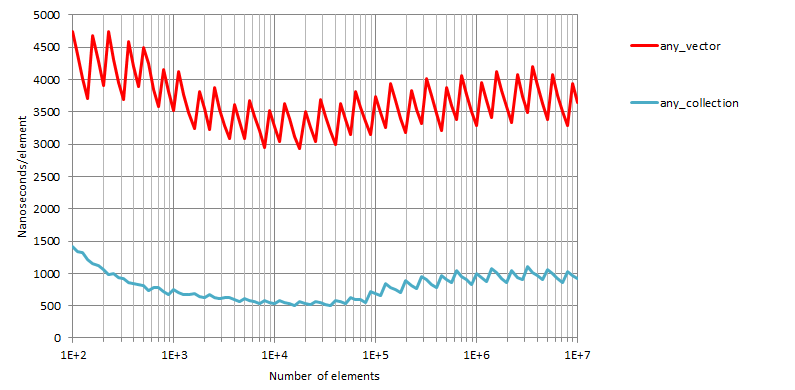 Insertion, Visual Studio
2022 x64
Insertion, Visual Studio
2022 x64
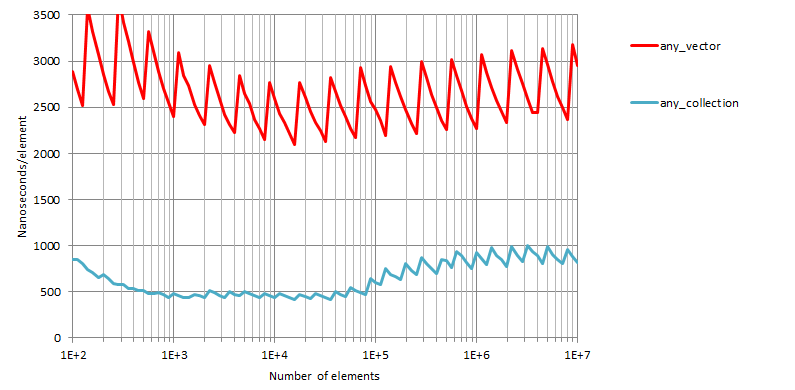 Insertion, GCC 13.2
x64
Insertion, GCC 13.2
x64
 Insertion, Clang 13.0
x64
Insertion, Clang 13.0
x64
 Insertion, Visual Studio
2022 x64
Insertion, Visual Studio
2022 x64
 Insertion, GCC 13.2
x64
Insertion, GCC 13.2
x64
 Insertion, Clang 13.0
x64
Insertion, Clang 13.0
x64
Tests measure the time taken to traverse a container of size n
(n between 102 and 107) and execute an operation on each
of its elements. The operation for boost::base_collection
and boost::function_collection (and the associated
baseline containers) is defined as
struct for_each_callable { for_each_callable():res{0}{} template<typename T> void operator()(T& x){ res+=x(2); } int res; };
whereas for boost::any_collection we use
struct for_each_incrementable { for_each_incrementable():res{0}{} template<typename T> void operator()(T& x){ ++x; ++res; } int res; };
and for boost::variant_collection we have
struct for_each_alternative { for_each_alternative():res{0}{} template<template<typename...> class V,typename... Ts> void operator()(V<Ts...>& x){ visit(*this,x); } template<typename T> void operator()(T& x){ ++x; ++res; } int res; };
The baseline container is tested with three different setups:
variant_vector as it is at equivalent
to the direct case (std::variant
does not allocate dynamic memory).
As for the polymorphic collection, three variations are measured:
std::for_each (the same as the baseline
container).
boost::poly_collection::for_each.
boost::poly_collection::for_each with type
restitution of T1,
T2 and T3.
The figures show resulting times in nanoseconds/element. The horizontal axis is logarithmic.
 Processing, Visual Studio
2022 x64
Processing, Visual Studio
2022 x64
 Processing, GCC 13.2
x64
Processing, GCC 13.2
x64
 Processing, Clang 13.0
x64
Processing, Clang 13.0
x64
 Processing, Visual Studio
2022 x64
Processing, Visual Studio
2022 x64
 Processing, GCC 13.2
x64
Processing, GCC 13.2
x64
 Processing, Clang 13.0
x64
Processing, Clang 13.0
x64
 Processing, Visual Studio
2022 x64
Processing, Visual Studio
2022 x64
 Processing, GCC 13.2
x64
Processing, GCC 13.2
x64
 Processing, Clang 13.0
x64
Processing, Clang 13.0
x64
 Processing, Visual Studio
2022 x64
Processing, Visual Studio
2022 x64
 Processing, GCC 13.2
x64
Processing, GCC 13.2
x64
 Processing, Clang 13.0
x64
Processing, Clang 13.0
x64